Mental health & addiction
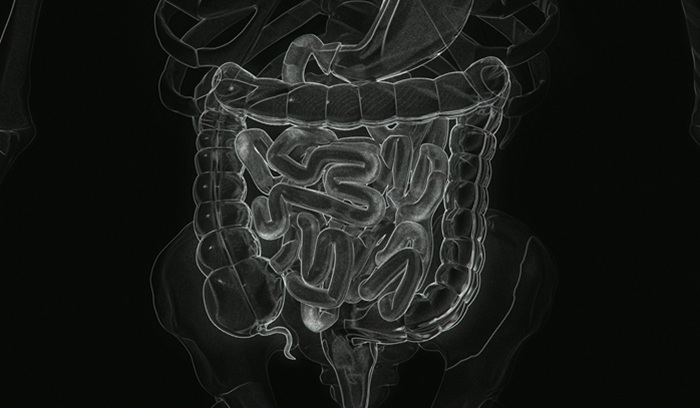
Fecal transplants reduce alcohol cravings as human trials progress
Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University have found that fecal transplants may help those suffering from severe alcohol use disorder. The work points to a compelling relationship between the gut microbiome and addiction disorders, with large-scale Phase 2 human trials currently underway. Nine of 10 patients who received a transplant had a reduction in their cravings and in the urine measurement of alcohol-related metabolites, compared to only three of the 10 placebo subjects displaying similar levels of improvement.
Finland bans smartphones in schools
The Finnish Parliament has approved a law restricting the use of mobile devices by pupils at primary and secondary schools. Pupils will need to get special permission from teachers to use their phones to assist them in studies, to take care of personal health-related matters, etc. Research increasingly indicates that excessive smartphone use in children and adolescents can negatively impact their mental and physical health, academic performance, and social development.
New Mexico becomes third U.S. state to legalize psilocybin therapy
Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham has signed SB 219 into law, effectively legalizing psilocybin-assisted therapy for qualifying patients across the state. The new law establishes a tightly regulated framework allowing for the medical use of psilocybin in treating conditions like treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, substance use disorders, and end-of-life anxiety. Under the program, therapy will consist of preparation, guided psilocybin therapy, and follow-up integration sessions. However, for everyone outside the program, possession and use of mushrooms is still a crime.
Brazil bans smartphones in schools to aim for better learning
Brazil’s Ministry of Education says that the restriction aims to protect students’ mental and physical health while promoting more rational use of technology. Institutions, governments, parents, and others have for years have associated smartphone use by children with bullying, suicidal ideation, anxiety, and loss of concentration necessary for learning. China moved last year to limit children’s use of smartphones, while France has banned smartphones in schools for kids aged six to 15.
Australia passes social media ban for children under 16
Australia has approved a social media ban for children aged under 16 after an emotive debate that has gripped the nation, setting a benchmark for jurisdictions around the world with one of the toughest regulations targeting Big Tech. The law forces tech giants from Instagram and Facebook owner Meta to TikTok to stop minors logging in or face fines of up to $32 million USD. A trial of methods to enforce it will start in January with the ban to take effect in a year.
Synapse-restoring pill set for human trials as novel schizophrenia treatment
Spinogenix is the American company behind the once-a-day pill that restored lost nerve cell connections in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Having been granted approval from the Australia Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC), it is now actively enrolling participants for its Phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate the safety, effectiveness, tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of once-a-day SPG302 as a treatment for schizophrenia.
U.S. overdose deaths plummet, saving thousands of lives
For the first time in decades, public health data shows a sudden and hopeful drop in drug overdose deaths across the U.S. National surveys compiled by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention already show an unprecedented decline in drug deaths of roughly 10.6% last year. That’s a huge reversal from recent years when fatal overdoses regularly increased by double-digit percentages.
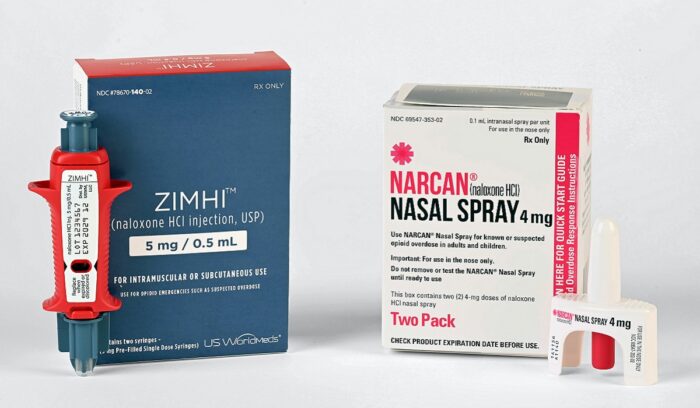
MIT scientists reverse opioid overdoses with ‘Narcan sensor’ implanted under skin
In 2023, more than 100,000 Americans died from opioid overdoses. The most effective way to save someone who has overdosed is to administer a drug called naloxone, but help can’t always reach the person in time. Researchers at MIT and Brigham and Women’s Hospital have developed a new device to address this problem. The device, about the size of a stick of gum, can be implanted under the skin. When it determines that an overdose has occurred, it rapidly pumps out a dose of naloxone.
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than any electrochemical sensor for the deadly drug
Synthetic opioids are one of the main drivers in overdose deaths in the United States. They are often mixed with other drugs, but because of their potency, they are often present in such small amounts that they can be hard to detect. The new sensor, developed by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, uses carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles to tell the most deadly drugs apart from others.